Where to Find Zinc, Why Your Body Needs It, and What Happens Without It Naturally
Do not be fooled by the industrial moniker; zinc is not something you would find in a hardware shop or rub on your nose at the beach. Zinc is a silent multipurpose agent inside the body that supports immune responses, aids in the magical closure of wounds, and even affects our senses of taste and smell.

Let us examine this underappreciated mineral in detail, including what it does for your body, how much you need, and where to get it without the need for supplements or sunscreen.
So, what exactly is zinc?
Since zinc is a trace mineral, your body can not function without it, but it does not require a lot of it. There is no pressure.
Beef, shrimp, pumpkin seeds, and even fortified breakfast cereals are good sources, according to Harvard School of Public Health nutrition specialist Teresa Fung.
Zinc's Unexpectedly Important Function in the Body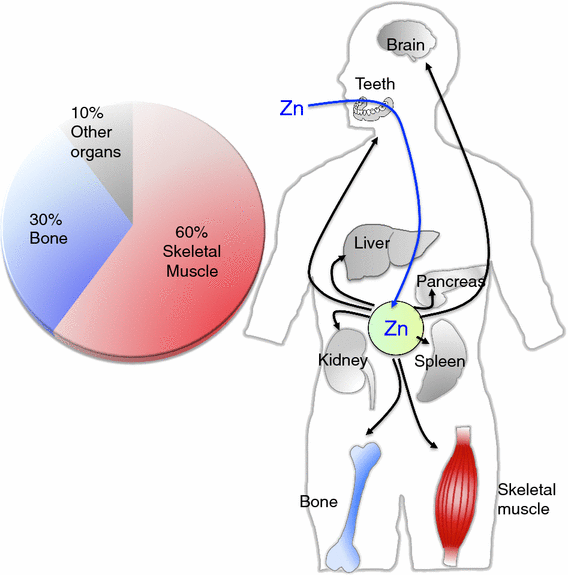
Zinc is referred to as the "immunity mineral," yet it is hardly an accurate description. Behind the scenes, this small nutrient is involved in several processes. Here's a sample of what it does:
Defense of the immune system: Zinc aids white blood cells in their function of warding off bacteria, viruses, and other unwanted visitors.
Healing wounds: Have you been cut? Zinc is a member of the team that is repairing your skin.
Hormone regulation: Zinc aids in the synthesis and equilibrium of several important hormones, including insulin and testosterone.
Reproductive health: Both proper fetal growth and sperm production depend on zinc.Sensory function: Your sense of taste and smell may entirely collapse if you do not get enough zinc.
Although it is not glamorous, it is definitely necessary.
In reality, how much zinc is required?
Let us dissect it:
Male adults: 11 mg daily
Women in adulthood: 8 mg daily
Women who are pregnant: 11 mg daily
Women who are nursing: 12 mg daily
With a diversified diet, most people can reach these numbers, but other groups are more likely to fall short (more on that below).
How Does Not Getting Enough Zinc Affect You?
Although zinc insufficiency is uncommon in the United States, when it does occur, the body begins to raise warning signs. Among the more revealing symptoms are:
Wounds that heal slowly
Loss of flavor or aroma
Skin issues (such as lesions or rashes)
Hair loss or thinning
recurring infections
Diarrhea
Insufficient appetite or dental health
A zinc deficiency in children might result in decreased growth and more frequent sickness episodes. Nevertheless, a blood test is the only reliable method to determine whether you are zinc deficient because these symptoms can potentially coexist with other medical conditions.
What's Your Reaction?




















